local-single-node-testnet
Goal
This section describes how to set up a single-node blockchain configuration running on a single host. This is referred to as a single host, single-node testnet. We will set up one node on your local computer and have it produce blocks. The following diagram depicts the desired single host testnet.
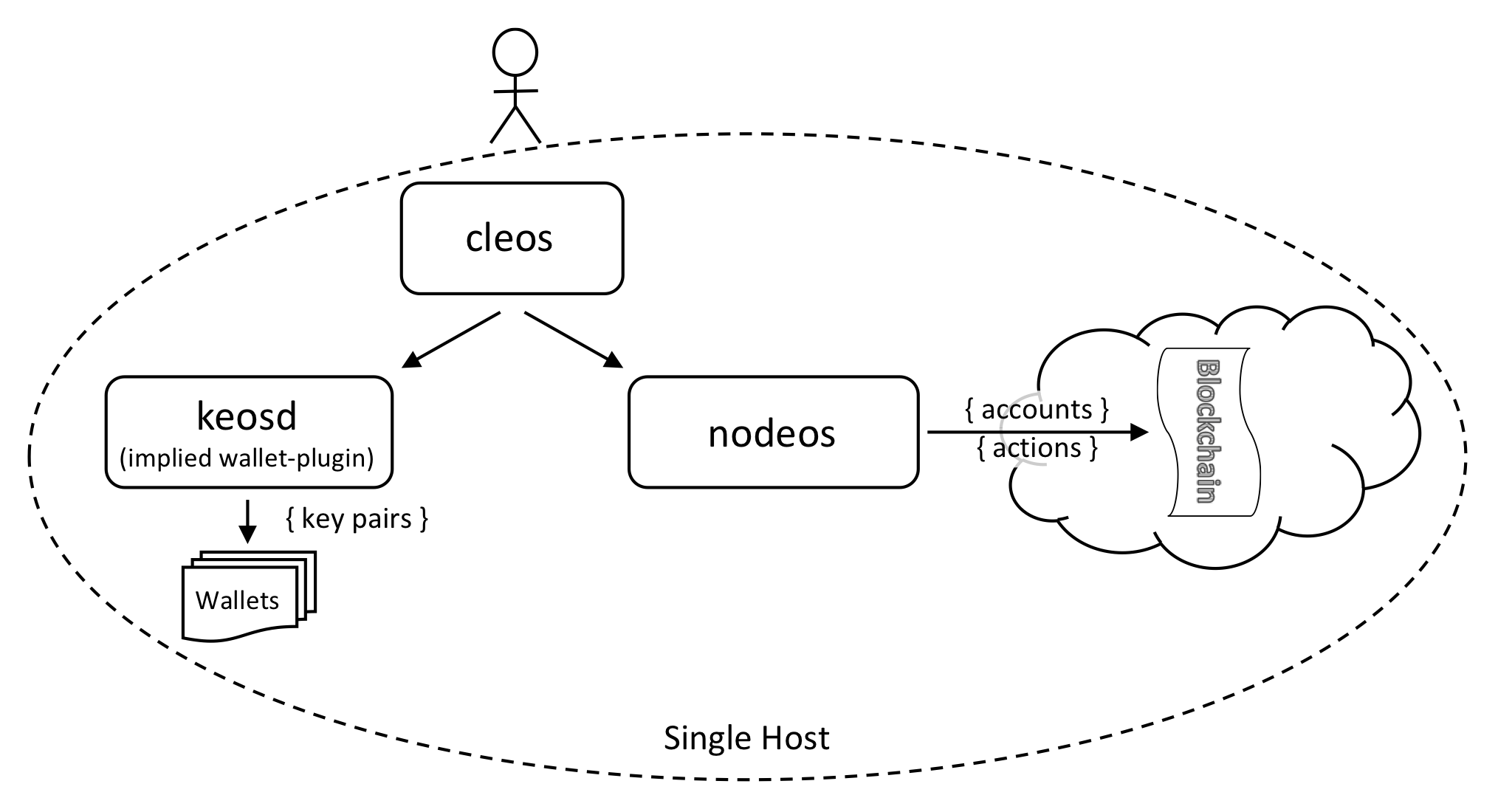
cleos is used to manage the wallets, manage the accounts, and invoke actions on the blockchain. keosd performs wallet management, including digital signing. If not started explicitly, keosd is started by cleos by default.
Before you begin
- Install the Antelope software before starting this section.
- It is assumed that
nodeos,cleos, andkeosdare accessible through the path.
- Know how to pass Nodeos options to enable or disable functionality.
Steps
Open one "terminal" window and perform the following steps:
1. Start the Producer Node
Start your own single-node blockchain with this single command:
nodeos -e -p eosio --plugin eosio::chain_api_plugin --plugin eosio::history_api_plugin
A minimal nodeos instance setup for block production requires both chain_api_plugin and history_api_plugin with the -e option (enable stale production) and -p eosio option (producer name eosio). Alternatively, you can also setup and specify your own account as the producer name.
After running nodeos, you should get log messages similar as below. It means the blocks are successfully produced.
1575001ms thread-0 chain_controller.cpp:235 _push_block ] initm #1 @2017-09-04T04:26:15 | 0 trx, 0 pending, exectime_ms=0
1575001ms thread-0 producer_plugin.cpp:207 block_production_loo ] initm generated block #1 @ 2017-09-04T04:26:15 with 0 trxs 0 pending
1578001ms thread-0 chain_controller.cpp:235 _push_block ] initc #2 @2017-09-04T04:26:18 | 0 trx, 0 pending, exectime_ms=0
1578001ms thread-0 producer_plugin.cpp:207 block_production_loo ] initc generated block #2 @ 2017-09-04T04:26:18 with 0 trxs 0 pending
...
eosio generated block 046b9984... #101527 @ 2018-04-01T14:24:58.000 with 0 trxs
eosio generated block 5e527ee2... #101528 @ 2018-04-01T14:24:58.500 with 0 trxs
...
At this point, nodeos is running with a single producer, eosio.
2. Get Node Info
Get info about the producing node:
cleos get info
This should produce output that looks similar to this:
{
"server_version": "0f9df63e",
"chain_id": "cf057bbfb72640471fd910bcb67639c22df9f92470936cddc1ade0e2f2e7dc4f",
"head_block_num": 134,
"last_irreversible_block_num": 133,
"last_irreversible_block_id": "00000085060e9872849ef87bef3b19ab07de9faaed71154510c7f0aeeaddae2c",
"head_block_id": "000000861e3222dce1c7c2cfb938940d8aac22c816cc8b0b89f6bf65a8ad5bdc",
"head_block_time": "2019-11-18T22:13:10.500",
"head_block_producer": "eosio",
"virtual_block_cpu_limit": 228396,
"virtual_block_net_limit": 1197744,
"block_cpu_limit": 199900,
"block_net_limit": 1048576,
"server_version_string": "v2.0.0-rc2",
"fork_db_head_block_num": 134,
"fork_db_head_block_id": "000000861e3222dce1c7c2cfb938940d8aac22c816cc8b0b89f6bf65a8ad5bdc",
"server_full_version_string": "v2.0.0-rc2-0f9df63e1eca4dda4cb7df30683f4a1220599444"
}
Advanced Steps
The more advanced user will likely have need to modify the configuration. nodeos uses a custom configuration folder. The location of this folder is determined by your system.
- Mac OS:
~/Library/Application\ Support/eosio/nodeos/config - Linux:
~/.local/share/eosio/nodeos/config
The build seeds this folder with a default genesis.json file. A configuration folder can be specified using the --config-dir command line argument to nodeos. If you use this option, you will need to manually copy a genesis.json file to your config folder.
nodeos will need a properly configured config.ini file in order to do meaningful work. On startup, nodeos looks in the config folder for config.ini. If one is not found, a default config.ini file is created. If you do not already have a config.ini file ready to use, run nodeos and then close it immediately with Ctrl-C. A default configuration (config.ini) will have been created in the config folder. Edit the config.ini file, adding/updating the following settings to the defaults already in place:
# config.ini:
# Enable production on a stale chain, since a single-node test chain is pretty much always stale
enable-stale-production = true
# Enable block production with the testnet producers
producer-name = eosio
# Load the block producer plugin, so you can produce blocks
plugin = eosio::producer_plugin
# As well as API and HTTP plugins
plugin = eosio::chain_api_plugin
plugin = eosio::http_plugin
plugin = eosio::history_api_plugin
Now it should be possible to run nodeos and see it begin producing blocks.
nodeos
nodeos stores runtime data (e.g., shared memory and log content) in a custom data folder. The location of this folder is determined by your system.
- Mac OS:
~/Library/Application\ Support/eosio/nodeos/data - Linux:
~/.local/share/eosio/nodeos/data
A data folder can be specified using the --data-dir command line argument to nodeos.
We will explore how to setup and run a single-host, multi-node testnet.